ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) are systems created for the effective management of an enterprise and its resources, data and business processes. This group of IT systems is broader than, for example, CRM (Customer Relationship Management), which contains the client base and data on interaction with the client.
What is included in ERP
The enterprise resource management system consists of modules, each of which is responsible for certain processes in the company and can complement others. A standard ERP system may include various modules. For example, our solutions include the following:
CRM:
- collection and analysis of information about clients;
- building omnichannel systems;
- client behavior analysis systems to help managers when working with clients; tips and recommendations for product and service managers;
- automatic sending of offers and forecasting the likelihood of a transaction;
procurement and sales management, work with tenders:
- integration with the Public Procurement Portal;
- tracking key tender dates;
- obtaining information and auto-filling in the system;
document flow:
- automatic numbering and accounting of documents;
- storage of scanned copies in a unified register;
- integration with 1C;
- introduction of digital signature;
- building processes for approving documents depending on the terms of the transaction;
human resource management:
- modules for drawing up individual work plans, calculating bonuses depending on coefficients;
- modules for distributing applications depending on the priority and workload of employees;
- modules for working with external contractors, allowing you to attach the result of work as a file, accept or reject the work, and fix payment;
- forecasting systems that allow you to identify certain risks.
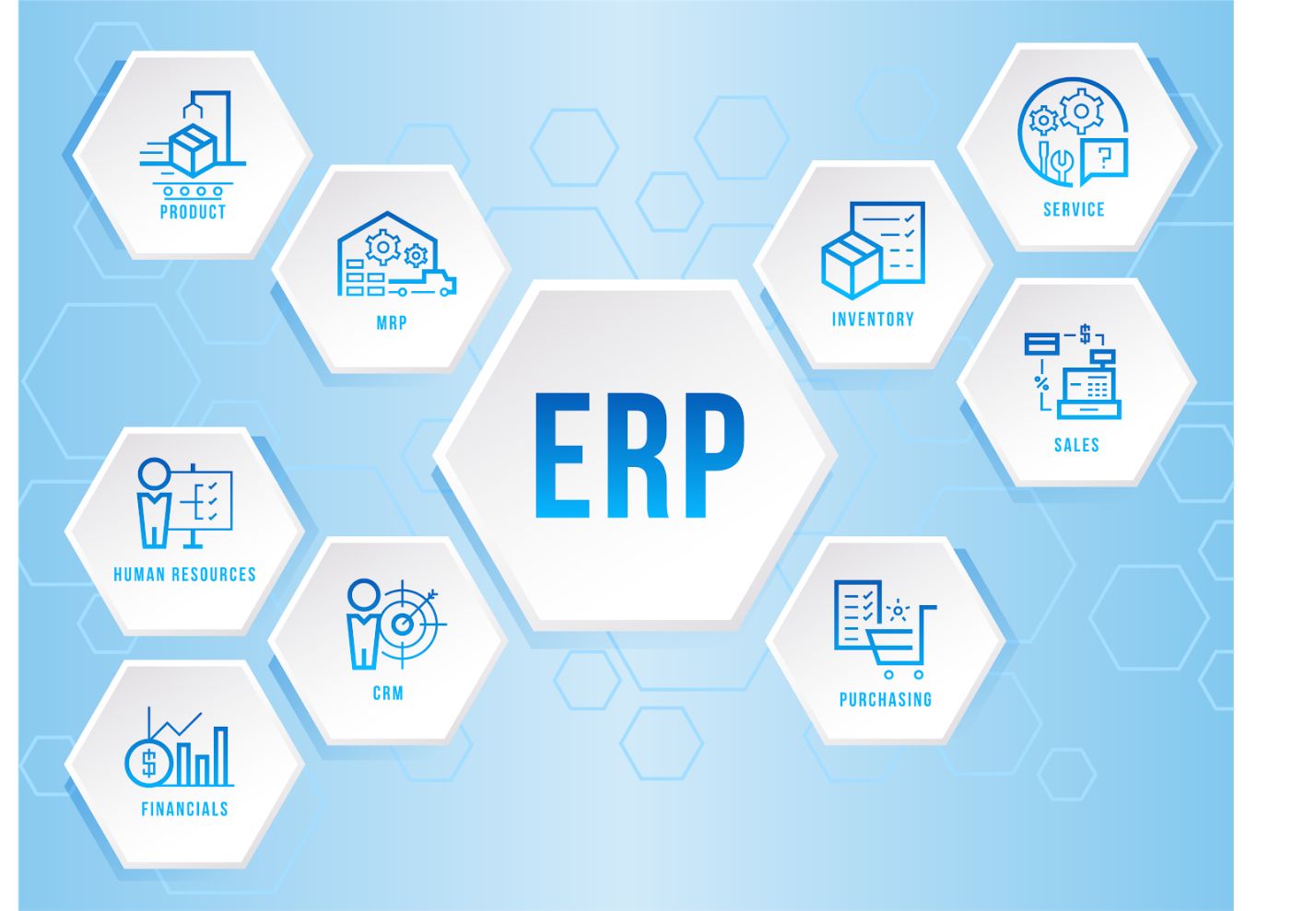
Depending on the needs of the company, ERP may include one or another set of modules to manage all internal business processes.
Types of ERP
Enterprise management systems can be divided according to various criteria; below are the most well-known groups of solutions:
- Complex ERP (for example, Oracle, Microsoft, SAP). These are universal ready-made systems that can be adapted for almost any business. As a rule, they are used by large companies, but integration is quite expensive and can take more than a year.
- Specialized ERP. Designed for a specific business area - for example, medicine, retail, passenger transportation, etc.
- Modular ERP. They can combine modules from several manufacturers, installed at different times and integrated with each other. Integration of such solutions often allows the company to save money, so it is suitable for small businesses.
When is an ERP system needed?
The need for an enterprise management system, as a rule, can be judged by the following criteria:
- Work efficiency and productivity decreases.
- Employees spend a lot of time performing tasks that can be automated.
- The company's business processes require the participation of specialists from different departments or units, integration with existing IT systems.
- The manager does not have sufficient means of control, planning and resource allocation.
IT solutions make it possible to simplify and automate any task, while at the start of developing an ERP system it is important to clearly define its tasks.

